Introduction to Filling Machines
In modern manufacturing and packaging, filling machines serve a vital role. These pieces of equipment are designed to dispense precise amounts of liquid, powder, or other materials into containers, ensuring consistency, speed, and efficiency in production lines. A well-designed filling machine can significantly enhance productivity and contribute to reduced operational costs while maintaining high standards of quality and safety.
What is a Filling Machine?
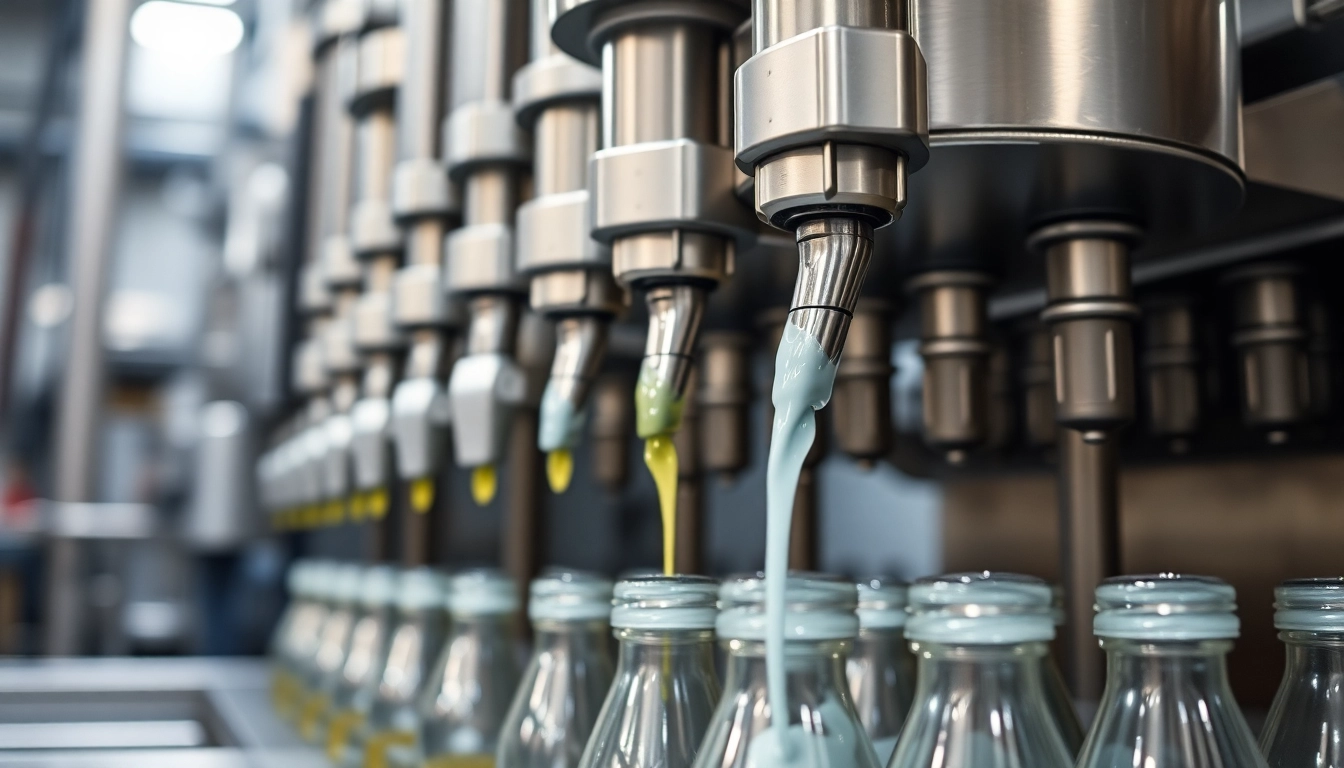
A filling machine is an automated or semi-automated device responsible for dispensing a specific volume of product into containers such as bottles, pouches, or jars. These machines can fill various materials, including liquids, powders, granules, and more. The filling process is essential across many industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and cosmetics, facilitating their product packaging needs.
Importance of Filling Machines in Production
Filling machines are crucial in production environments for several reasons:
- Efficiency: Automated systems allow for faster filling times compared to manual processes.
- Consistency: They ensure uniformity in the amount filled, thus minimizing waste and variations in product quality.
- Scalability: From startup operations to large-scale manufacturing, filling machines can be adjusted or scaled to meet varying production demands.
- Labor Savings: Automation reduces the need for extensive labor, allowing companies to allocate their human resources more effectively.
Key Components of a Filling Machine
Understanding the key components of filling machines helps in comprehending how they function effectively:
- Hopper: Stores the product that needs to be filled.
- Pump or Dispenser: Dispenses the product into the containers, driven by pneumatic, mechanical, or electronic systems.
- Control System: Allows operators to set and adjust parameters like fill volumes and machine speed.
- Conveyor System: Moves containers in and out of the filling station, integrating seamlessly with the production line.
- Safety Features: Includes sensors and alarms to detect issues during the filling process, ensuring operator safety and product integrity.
Types of Filling Machines
Filling machines can be categorized based on their operational functionality, filling method, and automation level. Understanding the differences is crucial for selecting the right machine for your application.
Manual vs. Semi-Automatic vs. Fully Automatic
Filling machines can be broadly classified into three categories based on the level of automation:
- Manual Filling Machines: These require human intervention for both loading the product and operating the filling mechanism. They are ideal for small businesses or low-volume settings.
- Semi-Automatic Filling Machines: These machines allow for some automation but still require human input for certain tasks. Operators might need to place containers and initiate the filling process automatically.
- Fully Automatic Filling Machines: Completely automated, these machines handle the entire process of receiving, filling, and sealing containers without human interaction, except for monitoring and maintenance.
Applications for Different Types of Filling Machines
Each type of filling machine caters to specific industries and product requirements:
- Manual Machines: Commonly used in artisanal food businesses or craft producers who require flexibility.
- Semi-Automatic Machines: Suitable for medium-sized enterprises looking for a balance between operation speed and manual control.
- Fully Automatic Machines: These are typically deployed in large-scale industrial settings, such as beverages and pharmaceuticals, requiring high output reliability and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Filling Machine for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate filling machine involves evaluating several factors:
- Product Type: Consider the viscosity, temperature sensitivity, and chemical properties.
- Container Type: The shape and material of the container affect machine design and operational mechanisms.
- Production Volume: Assess the expected fill rate and cycle time to choose the right automation level.
- Budget: Balance initial investment with long-term operational costs and efficiency improvements.
How Filling Machines Work
Understanding the operational mechanisms of filling machines provides insights into their effectiveness and reliability in production environments.
Mechanisms of Dispensing Liquid
The liquid dispensing process can generally follow these mechanisms:
- Gravimetric Filling: Measures the weight of the product as it is dispensed, allowing for high precision in totals.
- Volumetric Filling: Dispenses a specific volume of liquid using calibrated containers or pumps, suitable for uniform products.
- Pneumatic Filling: Uses air pressure to drive the filling process, ideal for thick or viscous liquids.
Calibration and Precision in Filling
Ensuring the filling machine is calibrated accurately is crucial for maintaining the quality and conformity of the fill. Regular maintenance and testing are required to uphold the required precision standards.
The calibration involves setting the machine to achieve specific fill volumes by adjusting the flow rate or pump cycle time according to the product characteristics. Following manufacturer guidelines and utilizing tracking software can help maintain consistent accuracy.
Maintenance Best Practices for Optimal Performance
To ensure smooth operation and extend the lifespan of filling machines, consider the following maintenance practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean all components to prevent contamination and ensure hygiene standards, especially in food and pharmaceutical applications.
- Routine Inspections: Check for wear and tear, ensuring all moving parts are lubricated and functioning correctly.
- Software Updates: Maintain any control software up-to-date to ensure optimal performance levels and reduce downtime from technical faults.
Industry Applications of Filling Machines
Filling machines are invaluable across several industries, each with unique operational requirements and challenges.
Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage sector utilizes filling machines specially designed for handling liquid, solid, and paste products. Different machines are used for various packaging forms such as bottles, cans, and pouches. Accurate filling is essential to comply with health regulations and consumer expectations.
Examples include:
- Alcohol and Beverage Filling: Machines that handle carbonated and non-carbonated drinks, ensuring precise fills and maintaining gas pressure.
- Condiments and Sauces: Machines designed to fill thicker products, preserving the product quality without spillage.
Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
Precision and hygiene stand out as significant factors in pharmaceutical and cosmetic filling processes. Machines handle various forms from liquids to creams, ensuring compliance with stringent industry regulations.
Applications include:
- Vials and Syringes: Specialized machines for accurately filling medicinal doses, crucial for patient safety.
- Cosmetic Fillings: Producing skincare or makeup products, ensuring precise fills and appealing presentation.
Automotive and Chemical Industries
In automotive and chemical manufacturing, filling machines cater to various compounds from oils to lubricants and hazardous materials. These machines must comply with numerous safety and regulatory standards.
Considerations include:
- Hazardous Material Filling: Specialized systems that manage toxic or flammable substances, ensuring safety in operation.
- Container Types: Machines accommodating various container sizes, making them adaptable to differing product inventories.
Enhancing Efficiency with Technology
To keep pace with demanding production environments and changing market needs, filling technology has evolved significantly in recent years.
Automated Features in Modern Filling Machines
Newer filling machines incorporate advanced automation features such as:
- Smart Sensors: Automatically detect the container alignment and filling status.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): Facilitate complex task management and adjustable settings based on product specifications.
- Touchscreen Interfaces: Improve user interaction, allowing operators to adjust settings and monitor performance in real time.
Data Tracking and Integration with Operations
Modern filling machines come equipped with data collection capabilities to track performance metrics:
- Output Metrics: Measuring the number of filled containers over time to assess efficiency levels.
- Quality Control: Providing data logs for traceability in case of product recalls or compliance checks.
- Integration with ERP Systems: Facilitating a unified approach to managing inventory, production, and order fulfillment.
Future Trends in Filling Machine Technology
The future of filling machine technology promises exciting innovations:
- Increased Automation: Full automation systems will handle more complex setups, offering real-time adaptability to production demands.
- Sustainability Innovations: Machines focused on reducing waste during the filling process and utilizing biodegradable materials.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Embracing the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Conclusion
Filling machines are a fundamental part of many industries, playing a critical role in the packaging and production processes. The advancements in technology and automation have not only increased efficiency but also improved safety, accuracy, and traceability. As companies continue to seek ways to optimize production, investing in the right filling machine tailored to specific needs can lead to significant competitive advantages in today’s market.